
What’s BRC-20 Ordi Token? Price Prediction and Live Chart
May 4, 2023
What’s STRK (Starknet) Coin Valued at $8 Billion? Airdrop and Price Prediction
May 6, 2023How To Do Layer Zero Token Airdrop And Price Prediction?

Table of Contents
Layer Zero token has been very popular recently, and users are looking for ways to participate in the airdrop. What is Layer Zero token?
1. Layer Zero Token Fundamental Analysis
Common characteristics of popular high-quality tokens: 1. Clear market demand, addressing a specific pain point for users. 2. Over a billion dollars in funding (Dasman, 2021).
1.1 Competitive Advantage of Layer Zero
These two fundamental aspects ensure that the token has minimal risk of Rug Pull during issuance, but other risks still exist. Layer Zero primarily addresses the current issue of cross-chain interoperability for tokens. In addition to Ethereum, the market includes various public chains such as SOL, COSMOS, POT, AVA, Polygon, OP, and recently SUI. Each of these chains has its own ecosystem, wallets, and networks. This makes token circulation more challenging and requires cross-chain conversions through connecting bridges.
Traditional cross-chain bridge protocols have many security vulnerabilities, high costs, and slow speeds. Furthermore, not all public chains support cross-chain bridges (Rohrer & Tschorsch, 2021).
For example, if Ethereum (ETH) wants to cross-chain to the Solana network, it can only be exchanged for Sol tokens and used on the Solana network. This means users have an additional token in their wallet. To use Ethereum on the Solana network without the need for exchanging to Sol tokens, support for cross-chain bridges between ETH and SOL is required. In the above scenario, the operation process of the cross-chain bridge is as follows:
Step 1: Users store the ETH they need to use on the Solana network in the treasury of the ETH-SOL cross-chain bridge, which is a multi-signature smart contract.
Step 2: Based on the corresponding ETH, new tokens (e.g., SETH) are minted on the Solana network.
Step 3: Users use SETH on the Solana network.
If users want to withdraw their original ETH from the Solana network back to Ethereum, they would need to destroy the equivalent amount of SETH on the cross-chain bridge and receive the corresponding ETH.
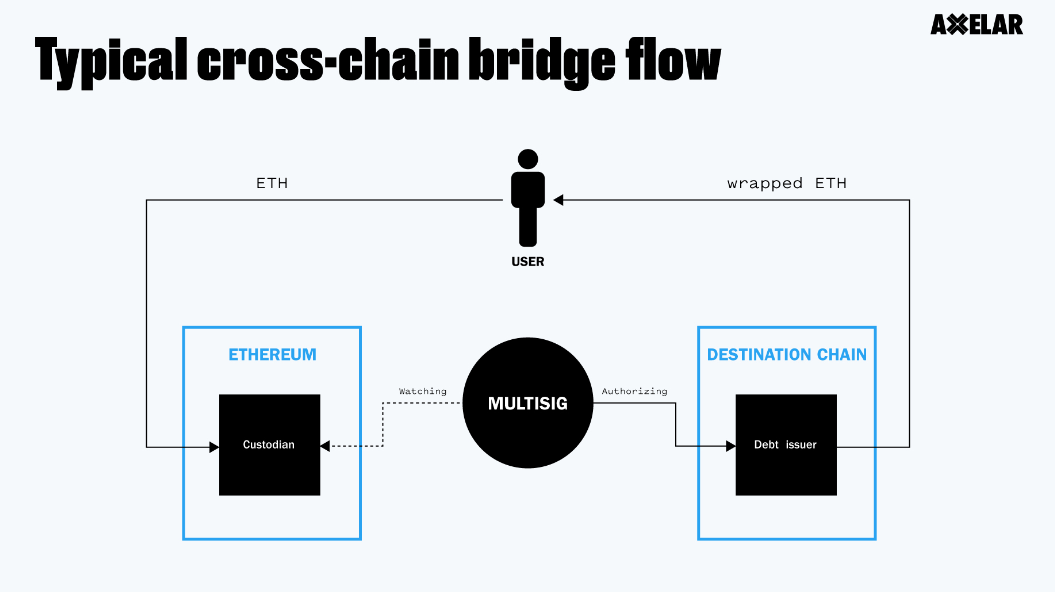
The cross-chain bridge protocol makes it easier to trade various tokens on DEXs and expands the possibilities of DeFi beyond the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing for token lending and borrowing beyond Ethereum-related tokens. This enables interoperability among tokens from different public chains (Developer, 2023).
However, traditional cross-chain bridges have significant security vulnerabilities. The major issue is the possibility of sending false tokens, allowing for minting on the cross-chain bridge and subsequent withdrawal. Another problem is that each token conversion requires verification on both networks, validating the block counts of the corresponding networks. This incurs high costs.
Vitalik Buterin also strongly opposes cross-chain bridges and advocates for multi-chain support rather than cross-chain interoperability.
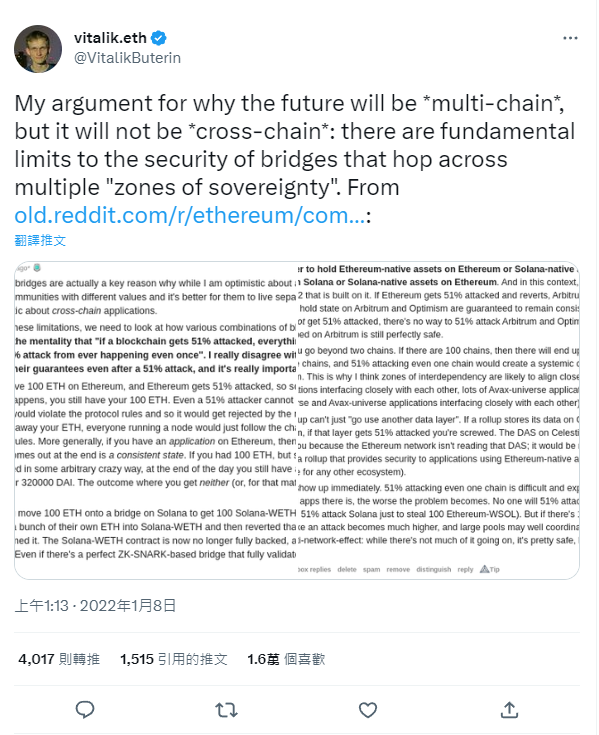
The key point is that no public chain currently has the capability to maintain its own chain while also being compatible with other chains. The development cost of such technology is too high, and with the increasing number of public chains, it becomes difficult to solely support the upgrades of these new chains.
At the same time, new public chains always surpass the old ones in terms of security and speed. New public chains are not interested in using the old ones because they believe in the superiority of their own technology and want others to use their solutions. Multi-chain is an idealistic and unrealistic approach.
The biggest problem lies in the fact that every time a new public chain emerges, there is a corresponding investment. With the rapid pace of blockchain technology, the limited funds in the capital market become fragmented due to the continuous emergence of new public chains, leading to reduced efficiency. Cross-chain interoperability truly addresses this issue by providing decentralized liquidity to the blockchain industry. It also means that Ethereum, the leading player in the smart contract market, will face stronger competition. This viewpoint goes against the mainstream market perspective and does not have a positive long-term outlook for Ethereum(Developer, 2023).
2.The Issues with Layer Zero
Layer Zero is considered an upgraded version of cross-chain protocols.
In traditional cross-chain protocols, Layer Zero adopts new technologies and architectures. The major upgrade is that it verifies partial blocks instead of the entire block. This significantly speeds up the cross-chain process and reduces the associated costs. Layer Zero verifies the headers of the blocks, whereas traditional protocols require the entire block to be verified on both networks. Partial verification requires the involvement of third parties. Layer Zero relies on third-party nodes and oracle mechanisms for partial verification.
2.1 Security of Layer Zero
Cross-chain protocols have inherent security vulnerabilities, and for Layer Zero, its security concerns mainly revolve around node and oracle verification. If both nodes and oracles engage in malicious verification, the issue of false tokens can reoccur. According to Layer Zero’s mechanism, the chances of both nodes and oracles engaging in malicious verification simultaneously are very low unless a node and an oracle collude. If such collusion occurs, it would be difficult to quickly identify stolen transactions, resulting in significant losses. Once such a problem arises, it is foreseeable that Layer Zero would be completely terminated(Developer, 2023).
From a technical perspective, this is one of the risks associated with Layer Zero.
3. Layer Zero Ecosystem and Airdrops
Layer Zero’s ecosystem is well-known for its 8 projects: Stargate Finance, Altitude DeFi, Pendle, Tapioca, RDNT, Trader Joe, Mugen Finance, and Rage Trade. Among them, Stargate is the flagship cross-chain project of Layer Zero. Users who hold Stargate token (STG) are eligible to receive cross-chain rewards. 45% of STG tokens are currently locked, and it is believed that with the issuance of Layer One tokens, the unlocking of STG tokens may happen earlier, leading to potential selling pressure.

Layer One’s airdrop is expected to be similar to ARB, where users need to perform certain actions on their chain, such as crossing over to Layer Zero through the official website. However, the official information does not specify whether there will be an airdrop, and it is only speculation that there might be one. Therefore, the conditions for the airdrop are unknown, and users can only rely on their previous experience with ARB airdrops to anticipate the potential airdrop in Layer Zero’s projects.
The following airdrop guide is for reference only and is not an official requirement. If you have participated in previous ARB airdrops, you should be familiar with the following steps:
- Stake $STG tokens on Stargate, any amount is acceptable.
- Cross chain to Stargate through LayerZero’s official website, preferably using USDC as LayerZero settles in USDC.
- Cross chain to Aptos.
- Cross chain to LiquidSwap.
- Cross chain to SushiSwap.
4. Price Prediction for LayerZero
In the first round of valuation, Layer Zero was valued at $1 billion with a funding of $135 million led by Sequoia Capital. In the second round, Series B funding amounted to $120 million, increasing the valuation to $3 billion. The total token supply has not been disclosed, so it is currently impossible to estimate the token price. Users can stay updated or bookmark this article for future announcements.
Price predictions will be published in subsequent updates below this article.
Reference
Rohrer, E., & Tschorsch, F. (2021). Blockchain Layer Zero: Characterizing the Bitcoin Network through Measurements, Models, and Simulations. Canada: IEEE. Retrieved from IEEE.
Dasman, S. (2021). Analysis of return and risk of cryptocurrency bitcoin asset as investment instrument. In Accounting and Finance Innovations. MPH.
Developer. (2023). Retrieved from LayerZero Network: https://layerzero.network/developers



